Category: News
Susan Lozier speaks at Session 2 of TED Countdown Summit
Oceanographer Susan Lozier dives into the importance of the ocean’s natural circulation, which overturns water in a way that naturally captures carbon and regulates global temperatures. She shares the incredible research being done internationally to track changes in this overturn, as warming global temperatures could slow the circulation, lessen carbon uptake and increase the rate of climate-related disasters. While a collapse in this age-old system isn’t likely until 2100, Lozier warns of the dangers faced by future generations if we don’t change course now, calling for climate action to lower temperatures within the next 10 years.
Read more: https://blog.ted.com/lessons-notes-from-session-2-of-ted-countdown-summit-2023/
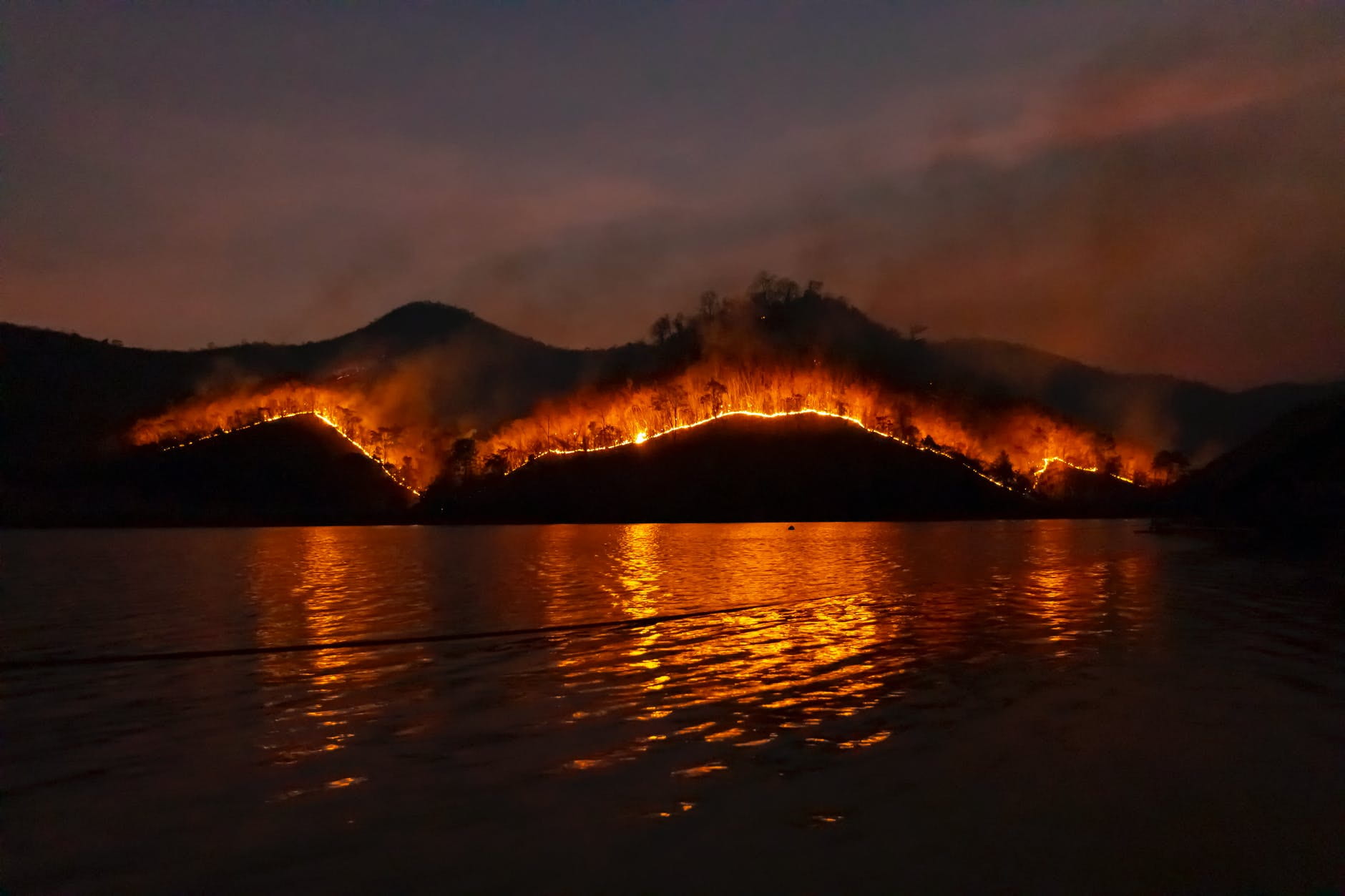
2021 brought a wave of extreme weather disasters. Scientists say worse lies ahead.
By Sarah Kaplan and Brady Dennis
There are millions of tips out there on “The weather of the past will not be the weather of the future,” says a NOAA scientist. “As long as we are emitting greenhouse gases at a historically unprecedented rate, we should expect this change to continue.”
Scores of studies presented this week at the world’s largest climate science conference offered an unequivocal and unsettling message: Climate change is fundamentally altering what kind of weather is possible, and its fingerprint can be found in the rising number of disasters that have claimed lives and upended livelihoods around the world.
Record-shattering heat waves, devastating floods, scorching wildfires and persistent droughts are among the litany of catastrophes scientists say they can definitively link to human activities — primarily the burning of fossil fuels.
Read full article: https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2021/12/17/climate-change-extreme-weather-future/
The Atlantic’s vital currents could collapse. Scientists are racing to understand the dangers.
By James Temple
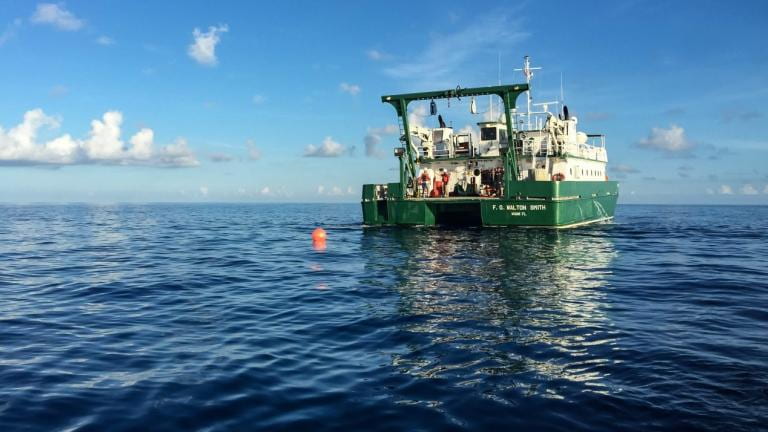
On a Saturday morning in December of 2020, the RRS Discovery floated in calm waters just east of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, the massive undersea mountain range that runs from the Arctic nearly to the Antarctic.
The team onboard the research vessel, mostly from the UK’s National Oceanography Centre, used an acoustic signaling system to trigger the release of a cable more than three miles long from its 4,000-pound anchor on the seabed.
The expedition’s chief scientist, Ben Moat, and others walked up to the bridge to spot the first floats as they popped up. The technicians on deck, clad in hard hats and clipped into harnesses, reeled the cable in. They halted the winch every few minutes to disconnect the floats as well as sensors that measure salinity and temperature at various depths, data used to calculate the pressure, current speed, and volume of water flowing past.
The scientists and technicians are part of an international research collaboration, known as RAPID, that’s collecting readings from hundreds of sensors at more than a dozen moorings dotting the Atlantic roughly along 26.5° North, the line of latitude that runs from the western Sahara to southern Florida.
They are searching for clues about one of the most important forces in the planet’s climate system: a network of ocean currents known as the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). Critically, they want to better understand how global warming is changing it, and how much more it could shift in the coming decades—even whether it could collapse.
Read full article: https://www.technologyreview.com/2021/12/14/1041321/climate-change-ocean-atlantic-circulation/
How the climate crisis played a role in fueling Hurricane Ida
Hurricane Ida made landfall last weekend near New Orleans as a Category-4 storm, lashing the region with winds of up to 150mph (240kph), heavy rains and several feet of storm surge on the 16th anniversary of Hurricane Katrina.
[…]
Several factors linked to the climate crisis are helping to fuel more powerful, destructive storms like Ida, scientists say.
The latest report from the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, the world’s leading authority on climate science, found that storms with sustained higher wind speeds – in the Category 3-5 range – have likely increased in the past 40 years.
The ocean absorbs over 90 percent of excess heat caused by greenhouse gas emissions from the burning of fossil fuels and that warm water feeds hurricanes.
“There is more energy available, so intensification of these hurricanes is expected,” Dr. Susan Lozier, president of the American Geophysical Union and an expert on the interaction of oceans, hurricanes and climate change, told The Independent. “And intensification brings more winds.”
More than a million people lost power when Ida toppled thousands of transmission lines and knocked 216 substations offline. Utility companies warned that thousands could remain in the dark and without air conditioning or running water for several weeks amid stifling heat and humidity.
Read full article: https://www.independent.co.uk/climate-change/news/hurricane-ida-louisiana-storm-katrina-b1912069.html
A Crucial System of Ocean Currents Is Faltering, Research Suggests
By Heather Murphy
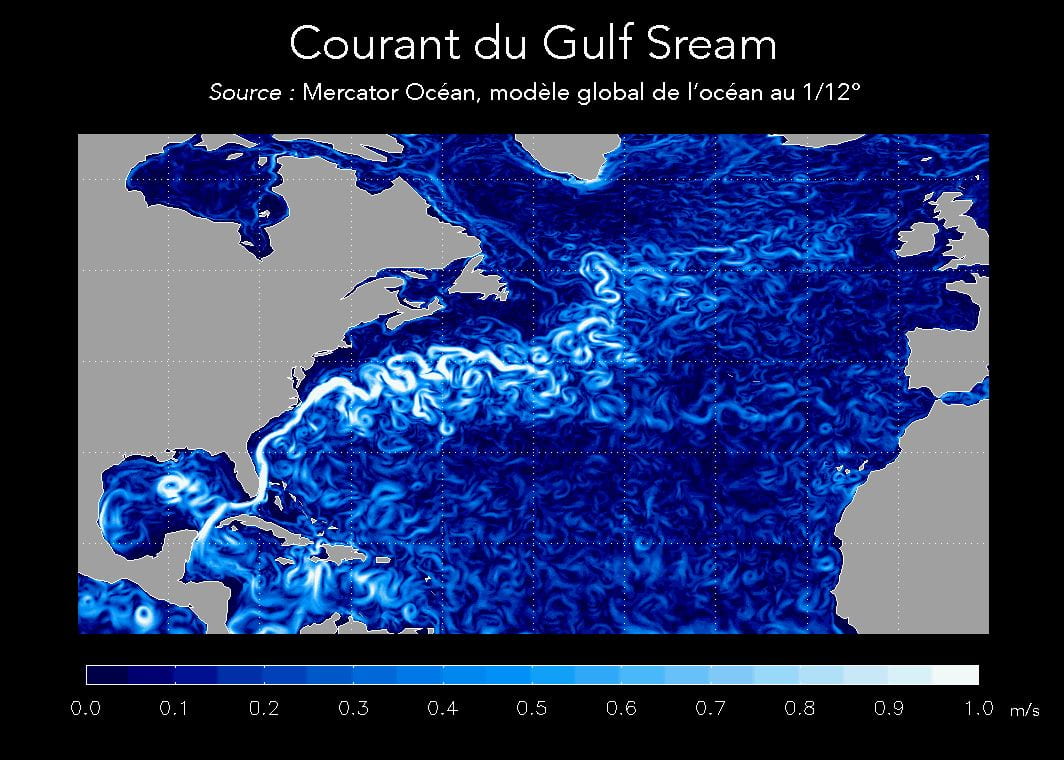
The water in the Atlantic is constantly circulating in a complex pattern that influences weather on several continents. And climate scientists have been asking a crucial question: Whether this vast system, which includes the Gulf Stream, is slowing down because of climate change.
[…]
Now, scientists have detected the early warning signs that this critical ocean system is at risk, according to a new analysis published Thursday in the scientific journal Nature Climate Change.
“I showed that this gradual slowing down of the circulation system is associated with a loss of stability,” said Niklas Boers, a researcher at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research in Germany, “and the approaching of a tipping point at which it would abruptly transition to a much slower state.”
[…]
[Susan Lozier] called Dr. Boers’ study “interesting,” but said she wasn’t convinced that the findings showed that circulation in that ocean system is slowing. “There are lots of things to worry about with the ocean,” she said, such as the more definitive concerns involving sea-level rise.
Read full article: https://www.nytimes.com/2021/08/05/us/gulf-stream-collapse.html
In the Atlantic Ocean, Subtle Shifts Hint at Dramatic Dangers
By MOISES VELASQUEZ-MANOFF and JEREMY WHITE
The warming atmosphere is causing an arm of the powerful Gulf Stream to weaken, some scientists fear.
[…]
It’s one of the mightiest rivers you will never see, carrying some 30 times more water than all the world’s freshwater rivers combined. In the North Atlantic, one arm of the Gulf Stream breaks toward Iceland, transporting vast amounts of warmth far northward, by one estimate supplying Scandinavia with heat equivalent to 78,000 times its current energy use. Without this current — a heat pump on a planetary scale — scientists believe that great swaths of the world might look quite different.
Now, a spate of studies, including one published last week, suggests this northern portion of the Gulf Stream and the deep ocean currents it’s connected to may be slowing. Pushing the bounds of oceanography, scientists have slung necklace-like sensor arrays across the Atlantic to better understand the complex network of currents that the Gulf Stream belongs to, not only at the surface, but hundreds of feet deep.
“We’re all wishing it’s not true,” Peter de Menocal, a paleoceanographer and president and director of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, said of the changing ocean currents. “Because if that happens, it’s just a monstrous change.”
Read full article: https://www.nytimes.com/interactive/2021/03/02/climate/atlantic-ocean-climate-change.html
Why is an ocean current critical to world weather losing steam? Scientists search the Arctic for answers.
BY CHERYL KATZ
A conveyor belt of ocean water that loops the planet and regulates global temperatures could be heading for a tipping point.
THE HIGH ARCTIC, ABOARD THE R.V. KRONPRINS HAAKON
Summer sea ice has been shrinking so dramatically here in the Fram Strait, high in the Arctic between Norway and Greenland, that researchers who make this trip annually point out missing patches like memories of departed friends.
“The first time I was here, in 2008, you could walk on the ice,” says Norwegian Polar Institute (NPI) oceanographer Paul Dodd, gesturing from the deck of this research icebreaker toward the spot, near the Prime Meridian, where his team is about to take samples for temperature, salinity, dissolved carbon, and other chemical measurements of what is now open water. It’s dotted with only a few random, battered-looking ice drifts.
Temperatures are rising and ice is melting all over Earth. But this place is special: The ocean changes that are happening right here could dramatically alter the climate for much of the rest of the planet.
Read full article: https://www.nationalgeographic.com/science/article/why-ocean-current-critical-to-world-weather-losing-steam-arctic#close
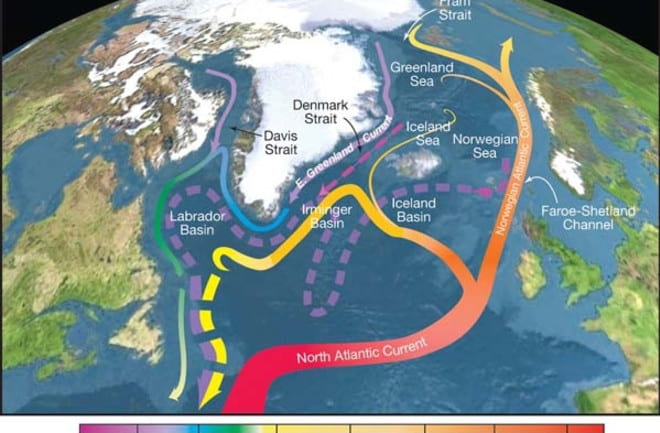
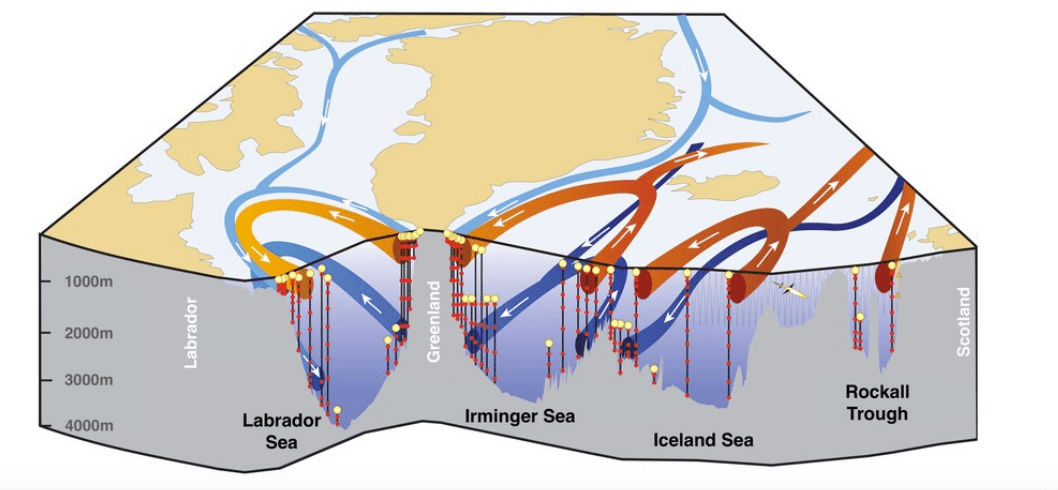
Major Study Rewrites the Driving Source of Atlantic Ocean Circulation
The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, shown here, serves as a conveyor belt that transports heat and pulls carbon from the atmosphere into the deep ocean.(Credit: R. Curry, Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution/Science/USGCR)
By Roni Dengler
Massive volumes of water circulate throughout the Atlantic Ocean and serve as the central drivers of Earth’s climate. Now researchers have discovered that the heart of this circulation is not where they suspected.
“The general understanding has been [that it’s] in the Labrador Sea, which sits between the Canadian coast and the west side of Greenland,” said Susan Lozier, a physical oceanographer at Duke University in Durham, North Carolina, who led the new research. “What we found instead was that … the bulk [of it] is taking place from the east side of Greenland all the way over to the Scottish shelf.”
The discovery will help improve global climate models.
Read full article: https://www.discovermagazine.com/environment/major-study-rewrites-the-driving-source-of-atlantic-ocean-circulation
A surprising new picture of ocean circulation could have major consequences for climate science
By Chris Mooney
Some experts say the Atlantic Ocean circulation is already slowing down — but we’re just beginning to learn how it really works.
It may be the biggest wild card in the climate system. Scientists have long feared that the so-called “overturning” circulation in the Atlantic Ocean could slow down or even halt due to climate change — a change that would have enormous planetary consequences.
But at the same time, researchers have a limited understanding of how the circulation actually works, since taking measurements of its vast and remote currents is exceedingly difficult. And now, a major new research endeavor aimed at doing just that has suggested a dramatic revision of our understanding of the circulation itself.
A new 21-month series of observations in the frigid waters off Greenland has led to the discovery that most of the overturning — in which water not only sinks but returns southward again in the ocean depths — occurs to the east, rather than to the west, of the enormous ice island. If that’s correct, then climate models that suggest the circulation will slow as the climate warms may have to be revised to take this into account.
The magnitude of the scientific surprise, on a scale of 1 to 10, is pretty large, said Susan Lozier, an oceanographer at Duke University who was lead author of the research published Thursday in Science.
Read full article: https://www.washingtonpost.com/climate-environment/2019/01/31/surprising-new-picture-ocean-circulation-could-have-major-consequences-climate-science/